Hitchcock TJ & Gardner A (in press) Paternal genome elimination promotes altruism in viscous populations. Evolution https://doi.org/10.1111/evo.14585

Image: https://www.craiyon.com
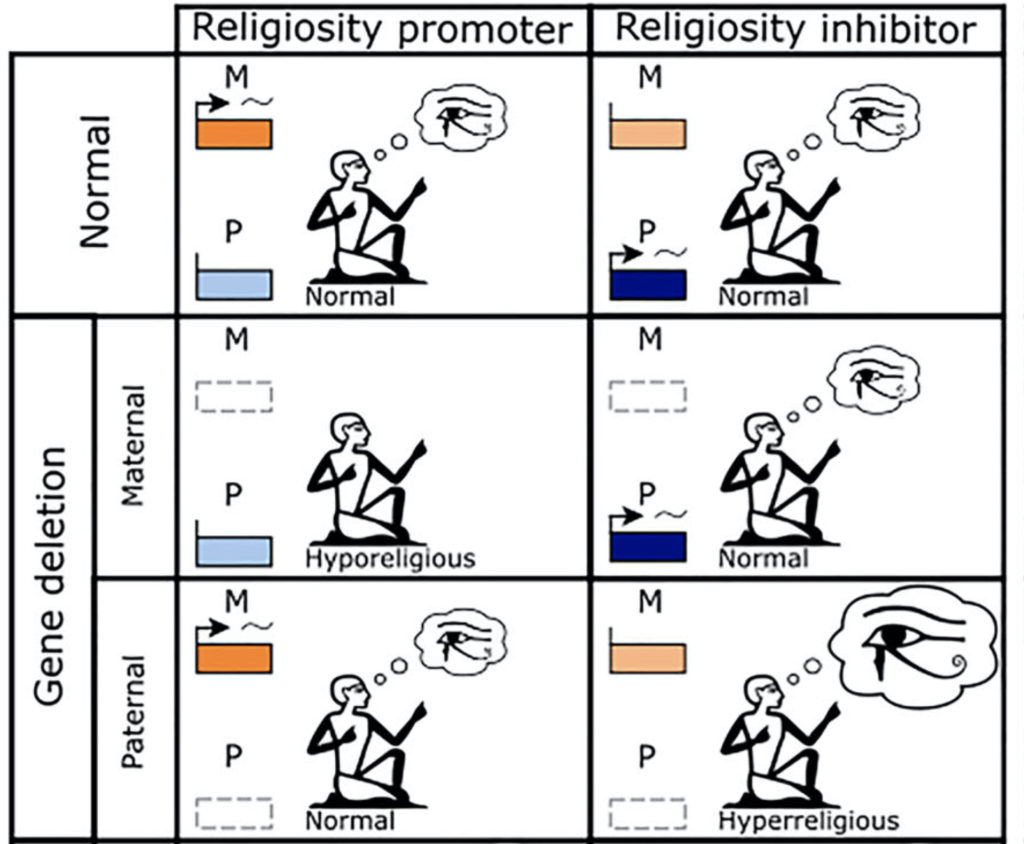
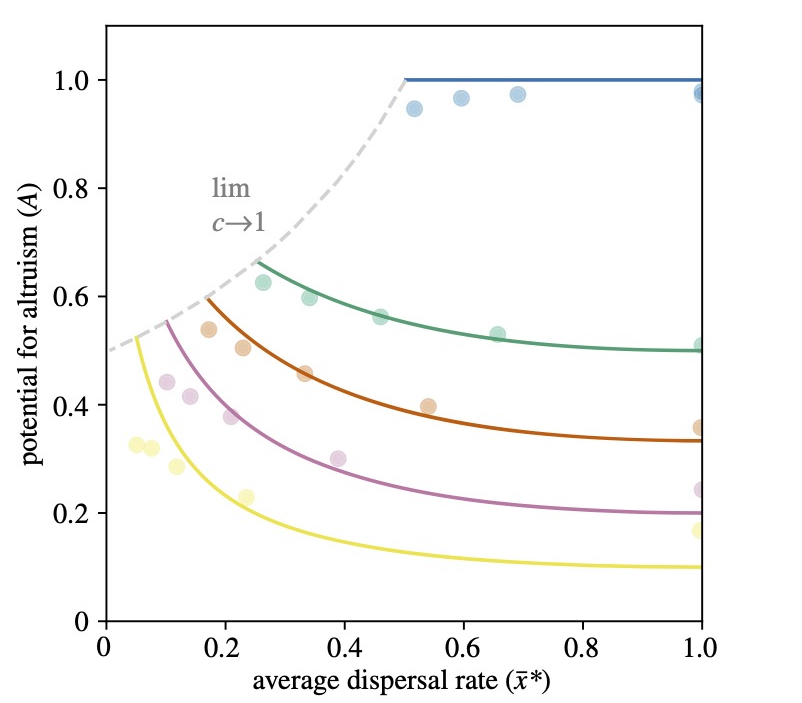
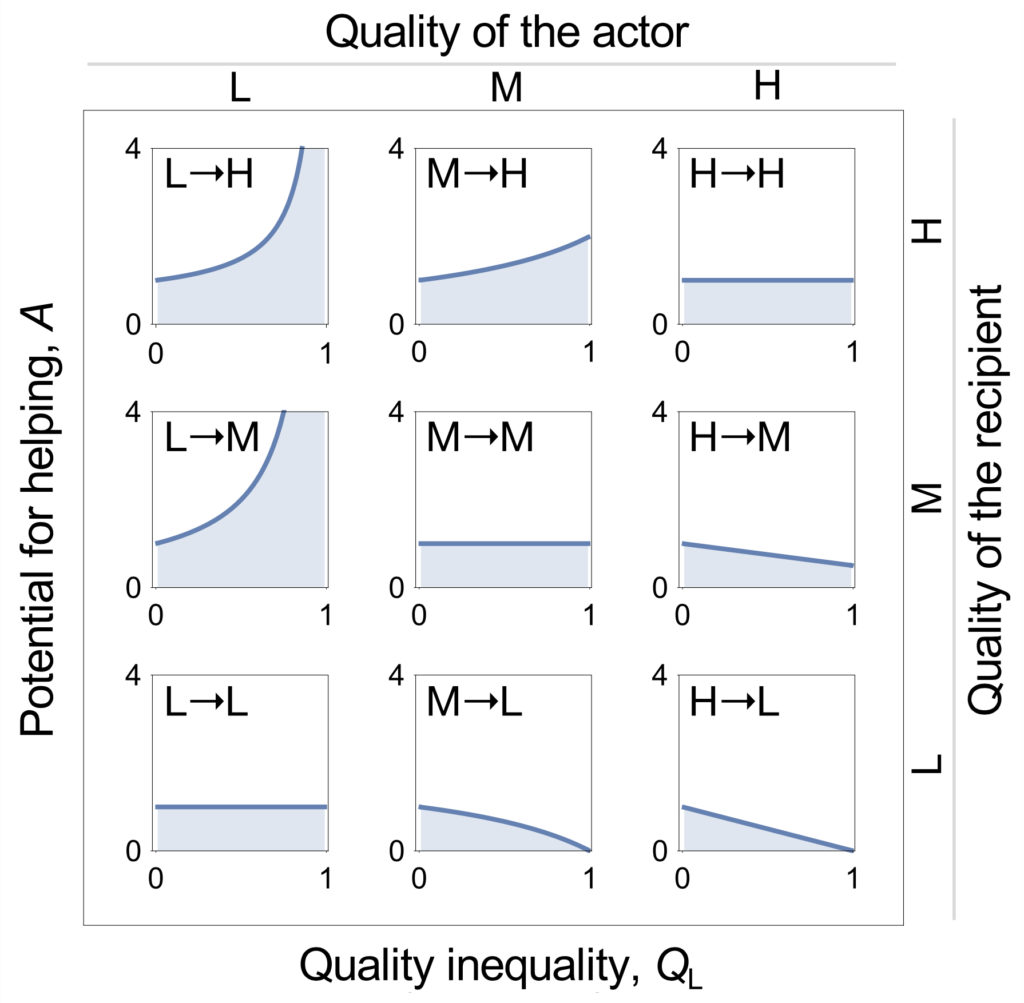
Population viscosity has long been thought to promote the evolution of altruism. However, in the simplest scenarios, the potential for altruism is invariant with respect to dispersal – a surprising result that holds for haploidy, diploidy, and haplodiploidy (arrhenotoky). Here we develop a kin-selection model to investigate how population viscosity affects the potential for altruism in species with male paternal genome elimination (PGE), exploring altruism enacted by both females and males, and both juveniles and adults. We find that: 1) PGE promotes altruistic behaviours relative to the other inheritance systems, and to a degree that depends on the extent of paternal genome expression. 2) Under PGE, dispersal increases the potential for altruism in juveniles and decreases it in adults. 3) The genetics of PGE can lead to striking differences in sex-specific potentials for altruism, even in the absence of any sex-differences in ecology.
Scots translation (by Ashley Douglas):
Paternal genome drap-oot forders altruism in stieve populations
Population stieveness has lang been thocht tae forder the evolution o altruism. Hooivver, in the maist straucht-forrit o scenarios, the potential fur altruism is invariant wi respeck tae skail – a stamagasterin ootcome that hauds fur haploidy, diploidy, and haplodiploidy (arrhenotoky). Here we pit forrit a kin-walin model fur tae airt-oot hoo population stieveness affects the potential fur altruism in species wi male paternal genome drap-oot (PGD), takkin tent o altruism enactit by baith females and males, forby baith young-anes and aulder-anes. We find that: 1) PGD forders altruistic ongauns relative tae the ither inheritance seestems, forby tae a degree that depends on the extent o paternal genome kythin. 2) Unner PGD, skail maks mair muckle the potential fur altruism amang young-anes and gars it less likely amang aulder-anes. 3) The genetics o PGD can lead tae kenspeckle differences in sex-specific potentials fur altruism, even wioot onie sex-differences in ecology.